Task Manager is one of the most frequently used tools in Windows 10. It’s a standard Windows 10 tool designed to manage the processes running on your PC. As a rule, it’s used to monitor the consumption of PC resources, as well as to force the termination of certain programs.
Since Task Manager is responsible for several basic operations in Windows, by default it’s limited to performing certain functions as an administrator for regular users as a security measure. The tool opens without additional permissions, but sometimes you may need to run Task Manager as an administrator on Windows 10 operating system. Well, let’s take a closer look at how to enter Task Manager as an admin on your Windows 10 PC or laptop in a few easy steps.
What is Task Manager?
The Windows operating system has many specialized tools that can be used to configure, control, and even repair certain programs or their processes. One such tool is the Task Manager. The Windows Task Manager is for monitoring programs and their processes. You can use it not only to see how busy your system is with processes but also to handle some failures and out-of-the-box situations.
Task Manager is a system monitor and startup manager that is part of Windows. It provides information about your computer’s performance and the apps you run, processes and CPU usage, memory load, and information about memory, network activity, statistics, logged users, and system services. Task Manager can also be used to set process priorities, and processor properties, start and stop services, and force processes to stop.
You can use Task Manager to start and stop programs and processes and gather statistics about your PC’s performance, network conditions, and the causes of system freezes and slowness, for example, when PUBG is lagging. If you’re interested in repairing your PC or having it crash, Task Manager will be an invaluable service. The main thing is to know how to use it.
Read Also:
- Windows 10 sleep mode not working – how to fix
- Taskbar volume icon not working on Windows 10
- How to fix Windows 10 “The Display Settings Could Not Be Saved”
How to run Task Manager as an administrator in Windows 10
Administrator rights give the user extended powers, to perform certain tasks. However, when a person opens a utility using the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl” + “Shift” + “Esc”, the PC doesn’t even ask the owner if he or she wants to run the app as an administrator. This makes many people feel that the extended rights in Task Manager make no sense at all.
However, in fact, this kind of startup opens up more possibilities for the user. Yes, you can close third-party software and control resource consumption without additional permissions. However, when it comes to system processes as well as malware, you won’t be able to shut it down without administrative rights.
Windows 10 users can create multiple Microsoft accounts, one of which will be administrative. Therefore, if you log into the OS as an administrator, all apps for you will start with extended permissions. If you have only one account, you can open the Task Manager in one of the two ways below.
How to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the Start button
If you want to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the Start button, you have to follow these steps:
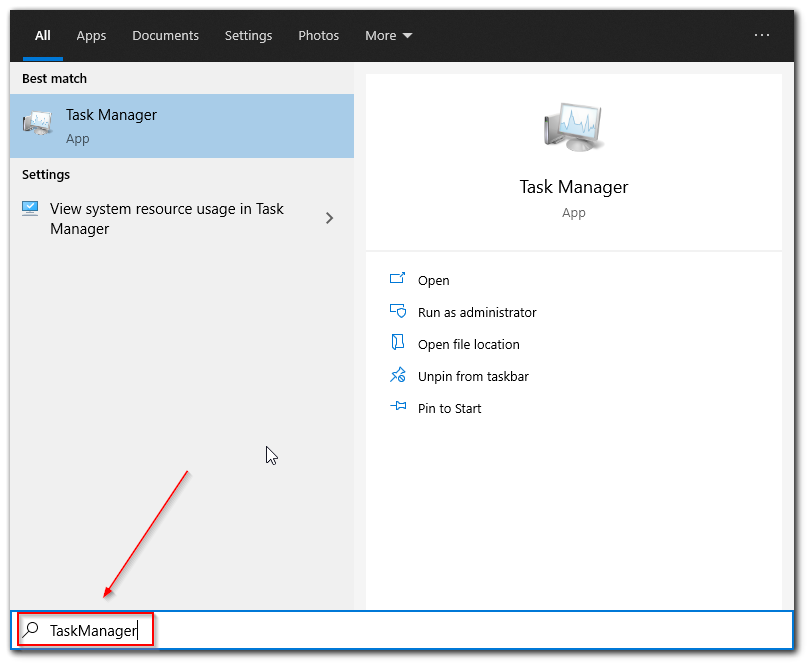
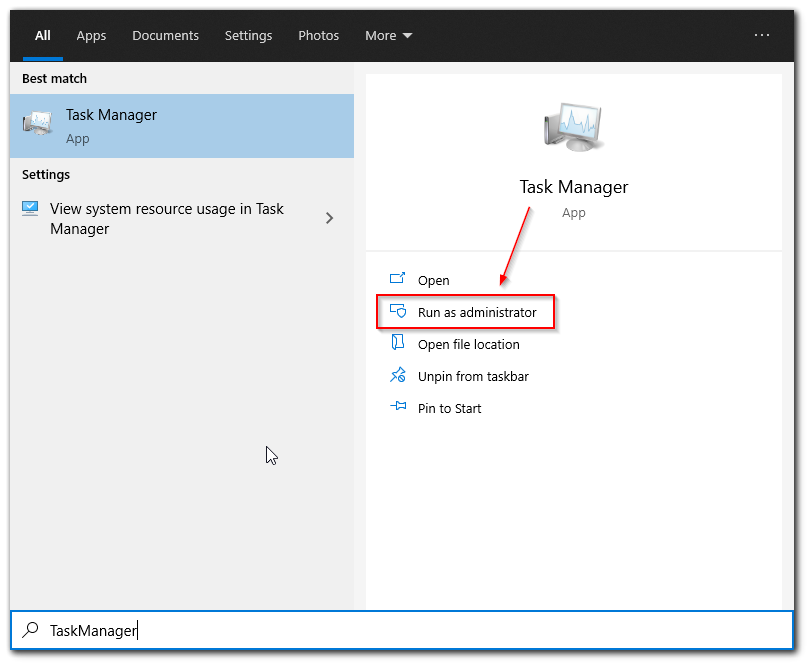
- First of all, click on the Start button and enter “Task Manager”.
- After that, just right-click on the “Task Manager” option and select “Run as administrator” from the list.
Once you have completed these steps, you will be able to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the Start button.
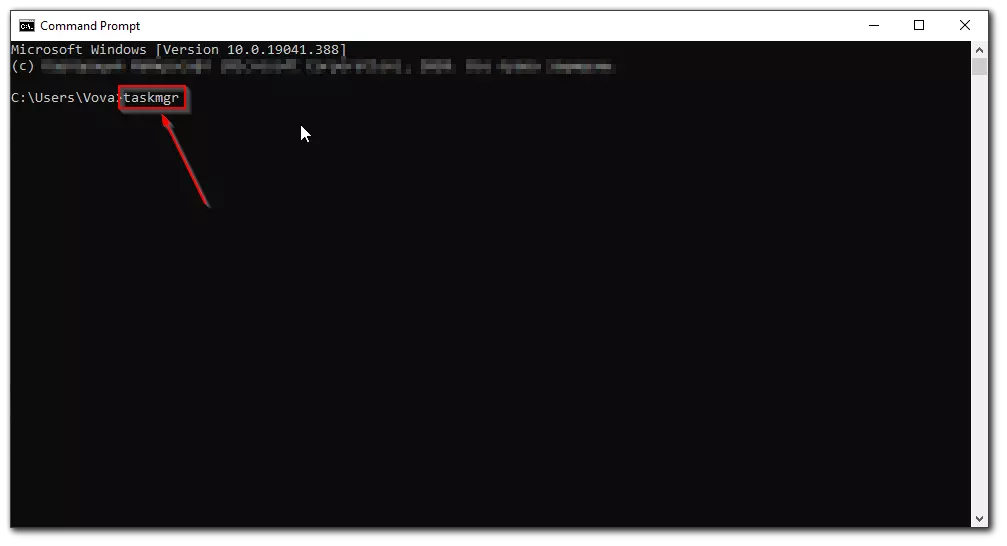
How to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the command prompt
If you want to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the command prompt, you have to follow these steps:
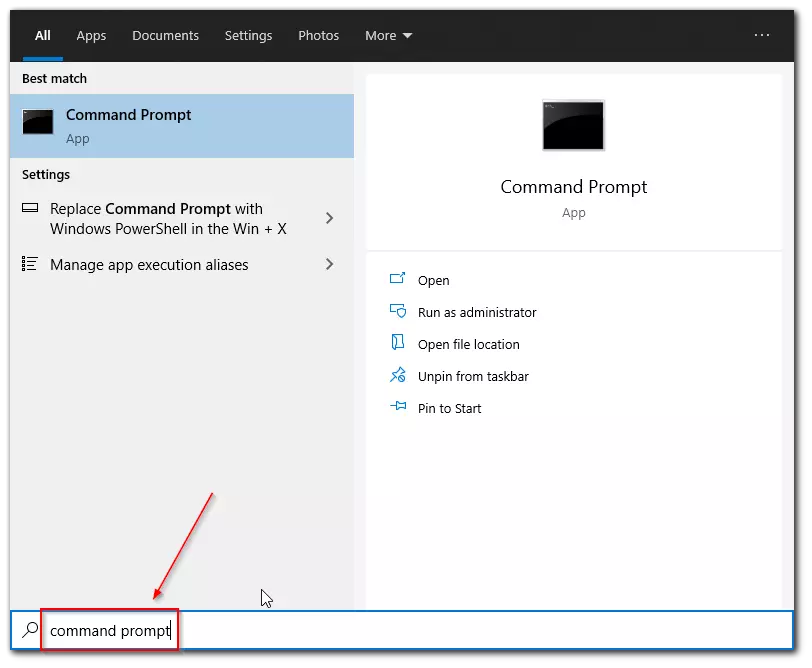
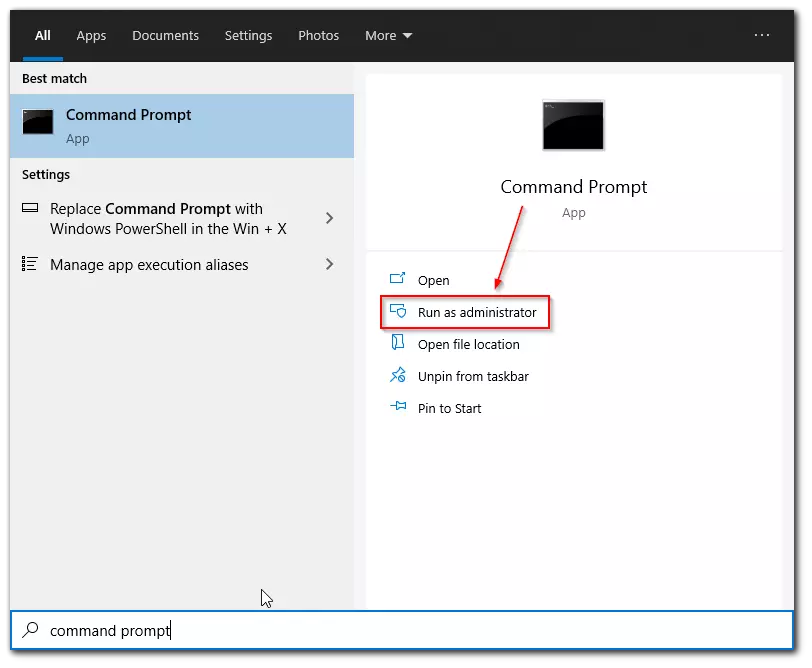
- Click on the Start button and enter “Command Prompt”.
- Then, just right-click on the “Command Prompt“ option and select “Run as administrator” from the list.
- Finally, in the command prompt that opens, enter “taskmgr” and press Enter.
Once you have completed these steps, you will be able to run Task Manager as an admin in Windows 10 using the command prompt. Moreover, you can also start Windows 10 in safe mode.
How to disable a frozen program using the Task Manager
The Task Manager is useful to novice users at least because it allows you to see which program is frozen and disable it. If some program doesn’t respond to our actions with the mouse, you have to press the cherished keys “Ctrl + Alt + Del” or “Ctrl + Shift + Esc”, and in the opened window of Task Manager on the tab “Processes” find this program, select it and press the bottom right button “End task”. And the frozen program will close.
Sometimes this method of closing the program doesn’t work. Then right-click on the program name and select “Go to details” in the drop-down menu, and in the next window right-click on the program line again and select “End process tree” in the list that appears.
How to manage app windows using the Task Manager
If you have several windows open in any app (for example, you have several Word documents open), you can use the Task Manager to manage them. To do this, click on the arrow to the left of the app, select the desired window, right-click on it, and select the desired action from the drop-down menu.
To do this, click on the arrow to the left of the app, select the desired window, right-click on it, and select the desired action from the drop-down menu:
- Switching
- Foreground
- Collapse
- Expand
- End task
Sometimes, you may also need to find your Windows 10 product key or digital license if Windows can’t identify your account when you upgrade your motherboard.
Read Also:
- What is Windows 10 0x800703ee error
- Is Windows 11 better than Windows 10 for gaming?
- How to fix System Thread Exception Not Handled in Windows 10
How to perform a system restore from the Task Manager
Sometimes it happens that no programs work and there’s no way to go to the desktop and the Start menu.
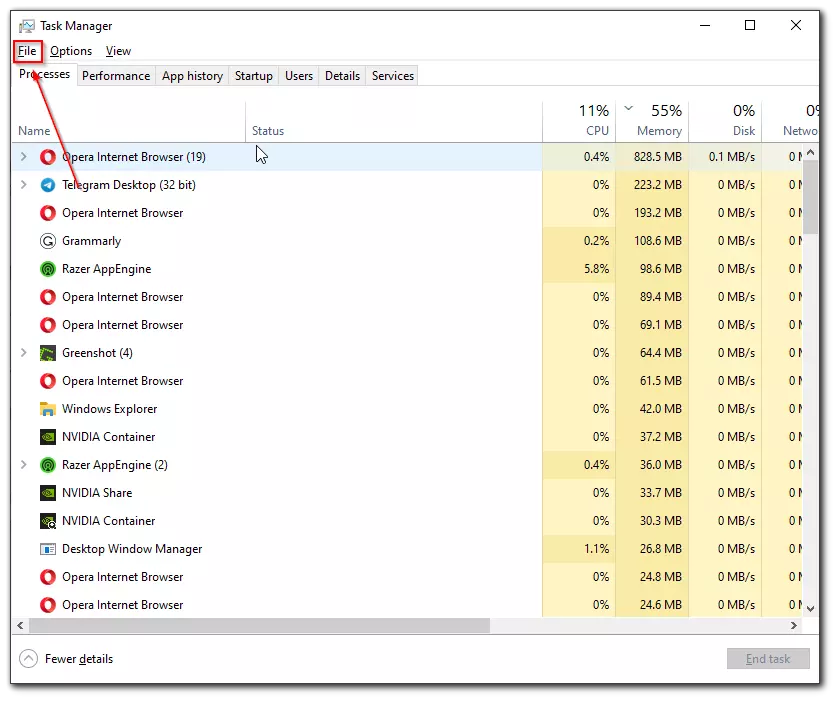
- In this case, you can launch the Task Manager, open the “File” menu, and select “Run new task”.
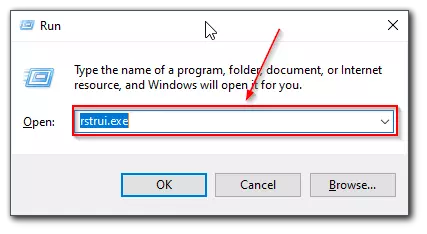
- In the “Run” window that opens, in the “Open” field, type the command “rstrui.exe”.
- And press the “OK” button.
- Finally, follow the instructions that will be displayed on the screen.
This command launches a system restore from previously created restore points. Very often this works, so you should not be lazy to create a restore point in case of global changes (installation of a new program or driver).