Many people have been wondering how to make their PC more automated. To set up automatic shutdown and start certain tasks at a specific time: to send an e-mail or create some macros (auto-execute keyboard or mouse actions). It turns out that almost all of this can be done with standard Windows tools, through the Task Scheduler.
A Windows system administrator has to perform the same operations every day – archive important data, diagnose the network, delete temporary files, etc. Many would like to automate all these processes. You can use Windows Task Scheduler for just such purposes. Windows Task Scheduler is a graphical utility built into the Windows OS that serves to run commands, scripts, and programs. Well, let’s take a closer look at how to run programs automatically using Windows Task Scheduler.
What is the Windows Task Scheduler?
Windows Task Scheduler is a service that can help automate the operation of your operating system. The automation environment can work both ways: you can set an app to start at a certain moment, or you can prevent the app from starting. For example, with the start of the operating system. You can also schedule updates, but that still won’t keep you safe from possible bugs that may be associated with Windows updates.
The difference between the Task Scheduler and Autorun, in this case, lies in the different spheres of Windows activity and greater rights for the Scheduler. This is often used by authors of malicious codes.
The Task Scheduler is an MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-in that can be used to assign various tasks to be performed at certain times or when certain events occur. Typically, such jobs are used to automate individual processes:
- Parametric automation of various tasks performed on the PC, e.g:
- automatically creating recovery checkpoints at specific times
- drive cleaning on specific days
- launching disk defragmentation at a certain time
- diagnostic testing
- Optimization of the PC boot process.
The Windows operating system contains several tools for scheduling jobs, including Task Scheduler, the Schtasks command line tool, and Windows PowerShell consoles. You can use these tools to schedule jobs on both local and remote workstations.
Read Also:
- How to fix Windows 10 sound speaker icon missing from the taskbar
- How to fix “Another program is using this file” in Windows 10
- How to fix Windows 10 “The Display Settings Could Not Be Saved”
How to plan a task using the Task Scheduler on Windows
The Task Scheduler is a free Windows tool that allows you to automatically run predefined Windows tasks. First introduced in Windows 95, this tool has stood the test of time. To schedule an automatic task on a Windows PC, you must first open Task Scheduler. Follow these steps to schedule a task:
- First of all, click on the Start button, enter “Task Scheduler” and open it.
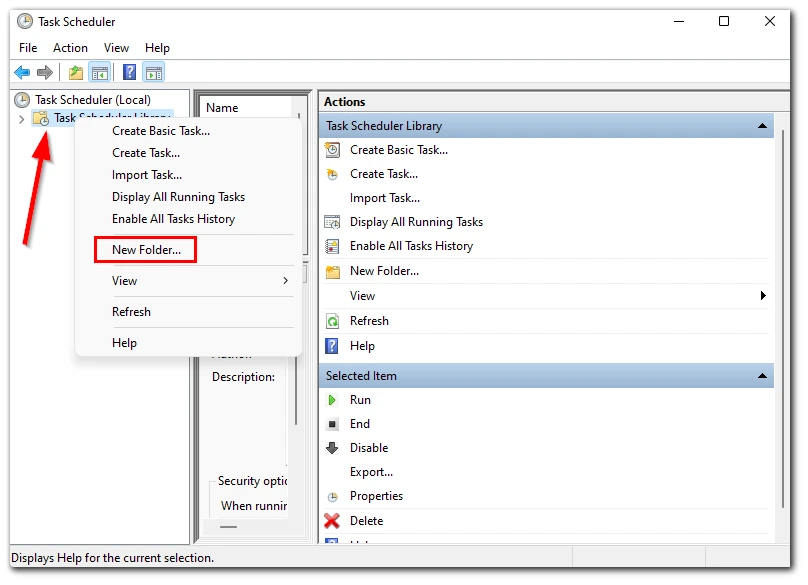
- Then, right-click on the “Task Scheduler Library” and select the “New Folder…” option.
- Now, enter the name of the new folder and click on the “OK” button.
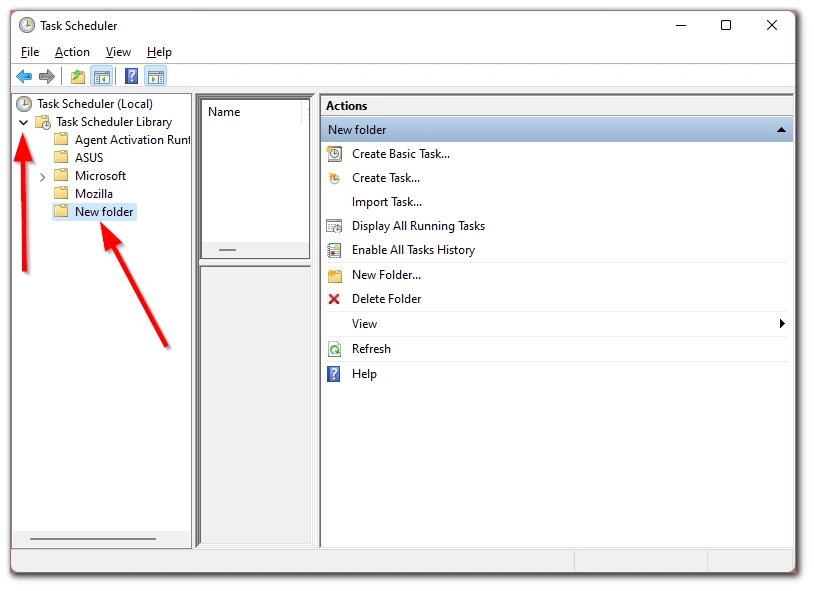
- After that, expand the “Task Scheduler Library” and go to the folder you created.
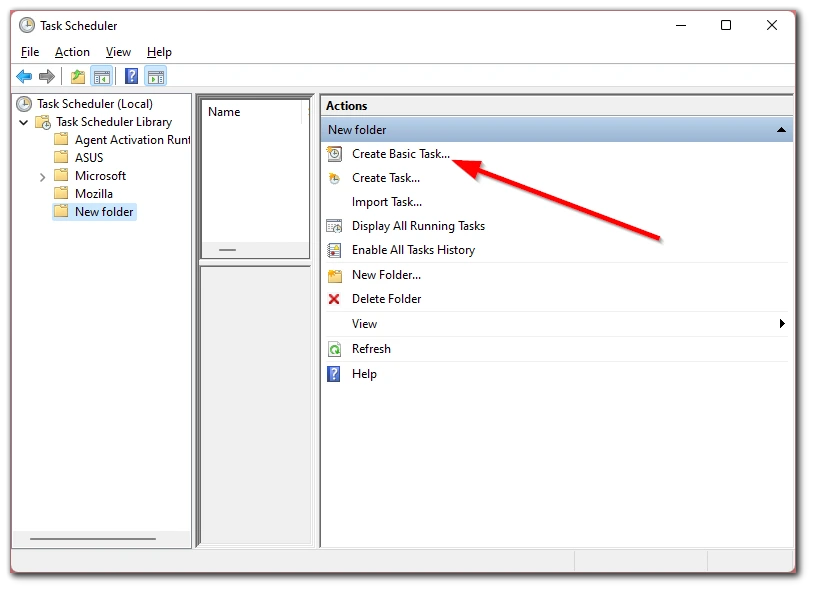
- Click on the “Create Basic Task…” option.
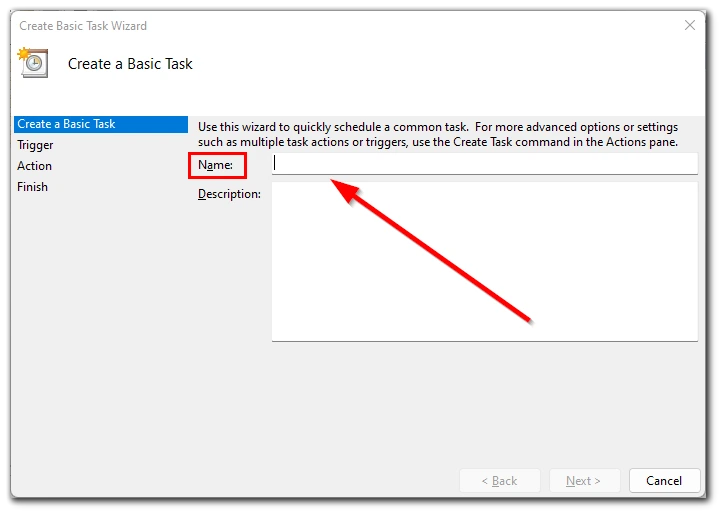
- In the Create Basic Task Wizard window, enter the task name and click “Next”.
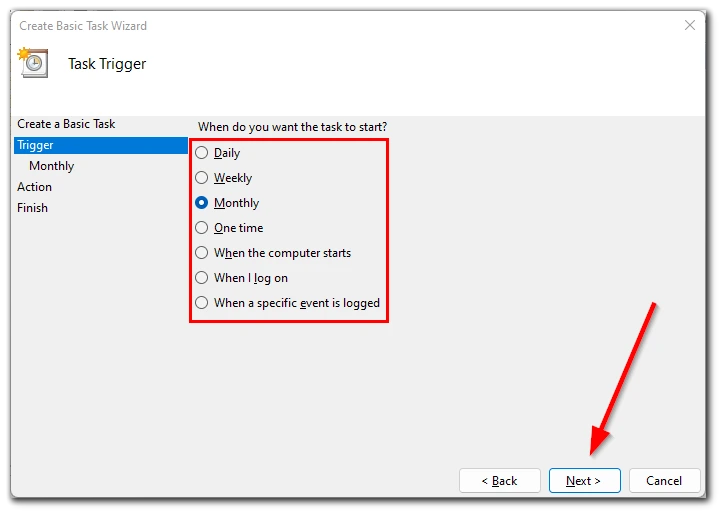
- Now you need to set a trigger. It determines how often your task will run. Set the trigger that works best for you and click “Next”.
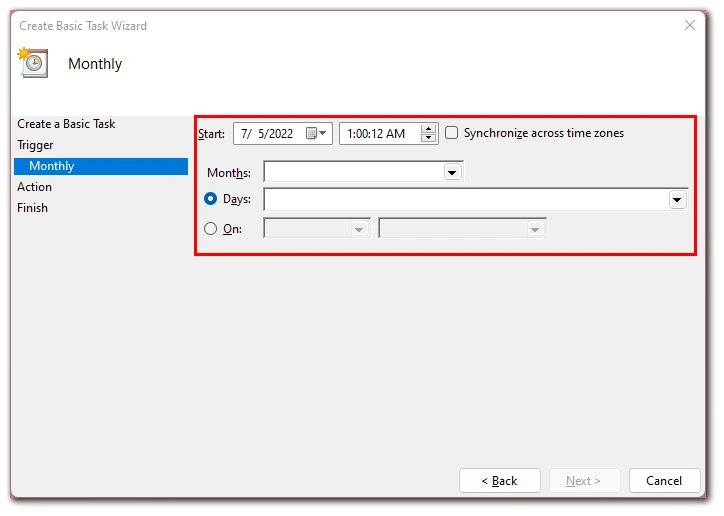
- Set the timings for the task and click “Next”.
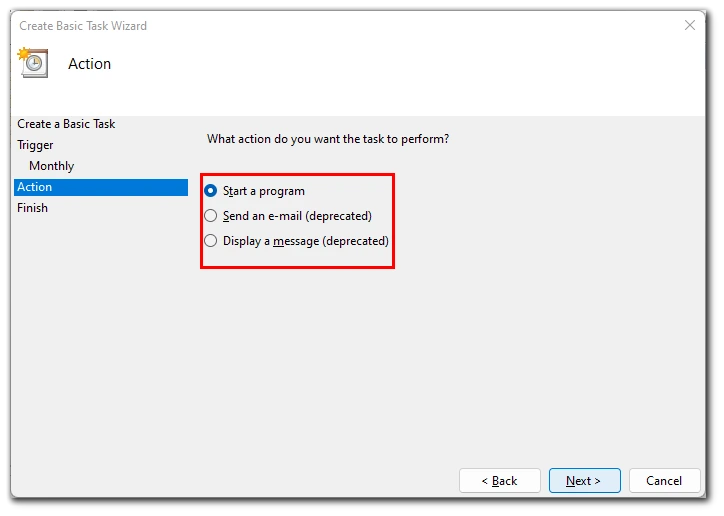
- Then select the action you want the Task Scheduler to perform. There are three actions to choose from: start a program, send an email, and display a message.
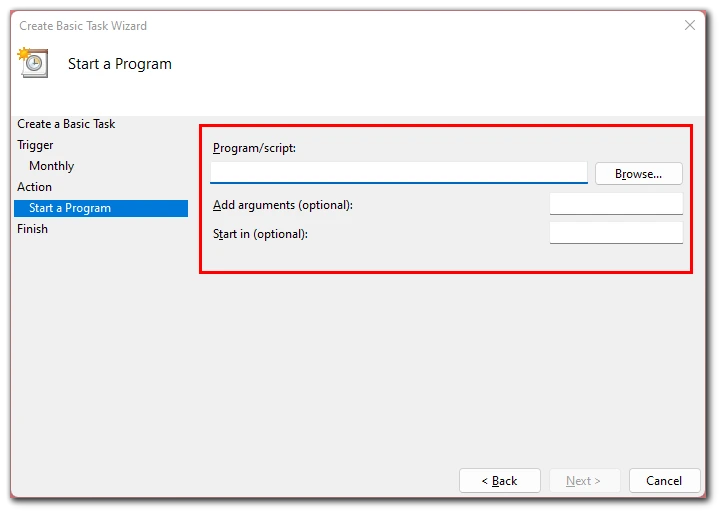
- Finally, just select the script that will launch your task and click “Finish” in the next window.
Once you have completed these steps, the task scheduler will create an automated task on your Windows PC. It will be run the next time your PC is booted up. Sometimes, you also need to clear the cache on your Windows 11 PC.
How to set up an automated task on Windows
Once you’ve created a task, you may always want to make changes to it at a later time. Fortunately, it’s pretty easy. Just go to the Task Scheduler main menu, and from there go to the folder you just created. Nothing new, just follow the same steps as above.
To make changes to automated tasks, simply right-click on the task you just created and select Properties. Once you do this, you will be taken to the properties section of your task. As you can see, here you can edit everything from general settings to triggers, actions, and more about your tasks.
How to delete your task using Task Scheduler
Task Scheduler is a handy app that lets you perform a wide range of automatic actions. From basic automation to scheduling your PC to wake up automatically, with Task Scheduler you can do it all. However, after it’s all said and done, you can also easily delete automated tasks.
Simply navigate to the automated tasks folder as you did in the previous step, right-click on the task, and select “Delete”. A confirmation dialog will appear and click “Yes” to proceed with the deletion.
Read Also:
- How to test your microphone on Windows 10
- How to enable/disable user account control (UAC) in Windows 11
- How to troubleshoot too quiet microphone on Windows 11
How to defragment a hard drive on Windows
Fragmentation is when blocks of data or fragments that make up a file are scattered all over the hard drive. This happens over time and slows down the system. Defragmentation is the process of merging these fragments into the physical space of the hard disk, which helps Windows quickly access such files.
Although Windows defragments your hard drive periodically by default, you should do it manually if you encounter excessive memory usage. Also, a modern SSD (solid-state drive) doesn’t require defragmentation, although you should perform the process on the hard disk (hard drive). To defragment a hard drive follow these steps:
- Click on the Start button and enter “Defragment and Optimize Drives”.
- After that, open this app and you will see a list of drives in your system or connected to it.
- Select the one you want to defragment and click “Optimize”.
The process will start immediately and will take time, depending on the storage and how fragmented the disk is. Wait for the process to complete, restart your PC, and check if your memory usage has decreased.