When considering storage options for laptops or other devices, terms like SSD and HDD often dominate the conversation. However, you might encounter devices equipped with eMMC storage, a less common but sometimes confusing option. Understanding the differences between eMMC and SSD storage can help you make an informed decision about which is better suited to your needs.
What Is an SSD and How Does It Work?
To properly compare SSDs and eMMC storage, let’s first delve into what SSDs are.
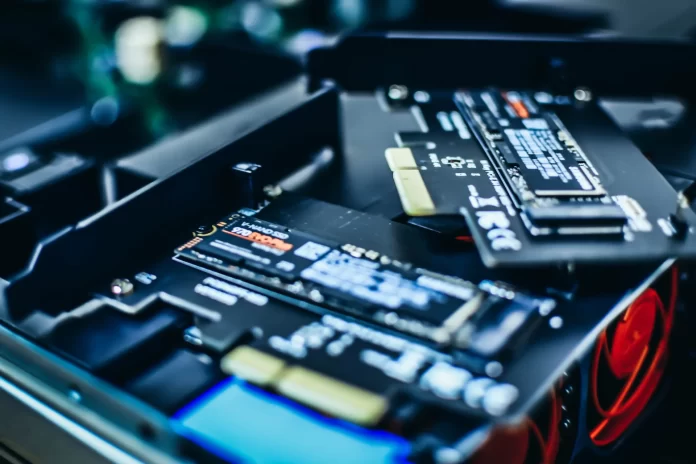
An SSD (Solid-State Drive) is a sophisticated piece of technology primarily composed of memory cells. Unlike traditional hard drives, SSDs have no moving parts, making them more durable and resistant to mechanical wear and tear.
One of the key advantages of SSDs is speed. Unlike a hard drive, which relies on spinning magnetic disks and moving heads to access data, SSDs can retrieve information almost instantly. This design eliminates the delays inherent in mechanical processes, allowing data to transfer significantly faster.
SSDs typically come in two popular form factors: the 2.5-inch SATA drive and the more compact M.2 drive. These have become standard in modern laptops, offering improved performance over traditional hard drives.
What Is eMMC and How Does It Work?
The term eMMC stands for Embedded Multimedia Card. Essentially, it functions similarly to the memory found in Micro SD cards or the internal storage of solid-state drives but on a simpler scale.
eMMC storage is most commonly found in mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Its design is straightforward and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for devices where affordability is a priority. However, eMMC storage generally offers lower capacity, with most drives topping out at around 128 GB. By contrast, high-end SSDs can offer terabytes of storage.
Unlike SSDs, eMMC storage is soldered directly onto a device’s motherboard. This design makes it non-removable and nearly impossible to replace or upgrade without professional assistance. In essence, eMMC acts as a built-in memory card for your device.
Key Differences Between eMMC and SSD Storage
Just a few years ago, SSDs were prohibitively expensive, making eMMC the logical choice for budget-friendly laptops and ultrabooks. However, with the dramatic reduction in SSD prices and their increased storage capacities, most modern devices now favor SSDs. That said, eMMC remains a staple in smartphones, tablets, and other compact devices.
Performance and Cost
The primary differences between eMMC and SSD storage lie in their speed and price. SSDs are considerably faster than eMMC drives but also more expensive. The speed advantage of SSDs comes from their ability to read and write data across multiple flash cells simultaneously. In contrast, eMMC storage performs sequential read and write operations, which limits its speed.
eMMC storage has average sequential read speeds of around 100 MB/s and write speeds of about 40 MB/s. By comparison, SSDs can achieve read speeds of up to 1500 MB/s, depending on the model.
Capacity and Usage
eMMC storage is typically limited to smaller capacities, making it ideal for devices where minimal storage is sufficient. On the other hand, SSDs are available in a wide range of capacities, from modest sizes to multi-terabyte options, making them better suited for laptops and desktop PCs.
Similarities Between eMMC and SSD Storage
Despite their differences, eMMC and SSD storage share some common features. Both use NAND flash technology to store data, which allows for faster reading speeds compared to traditional hard drives. However, writing to either type of storage is slower than reading, as each flash cell must be cleared before new data can be written.