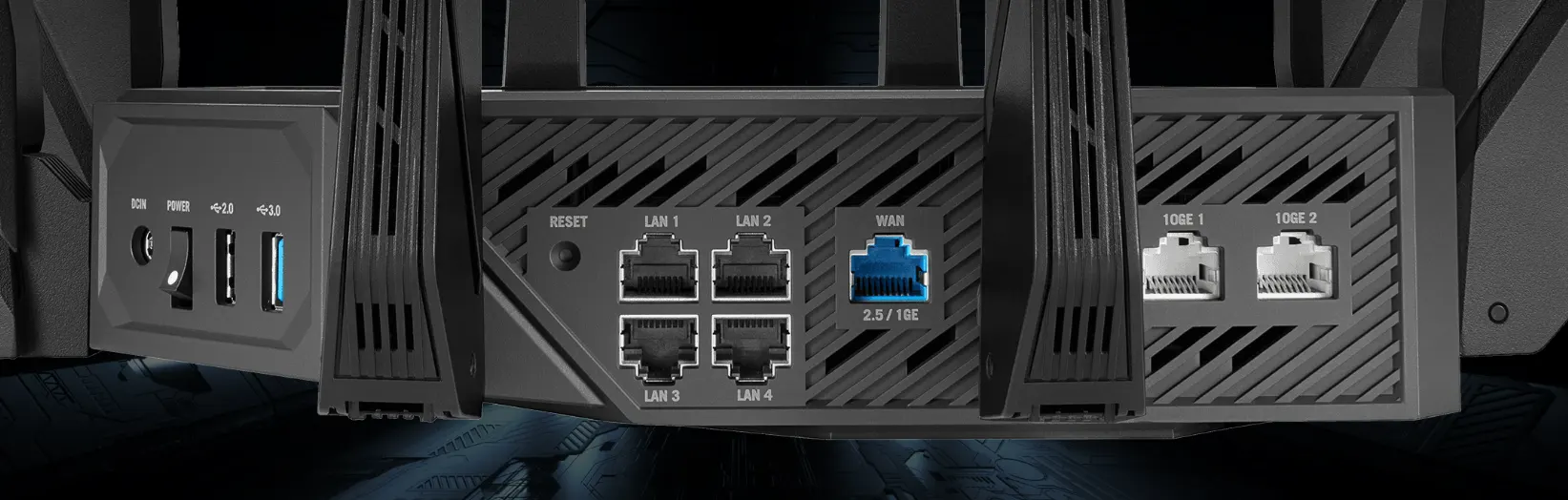
Modern high-end routers come equipped with various types of ports, each serving distinct networking purposes:
- WAN (Wide Area Network): The WAN port on a router is typically used to connect to a broadband internet service. This could be through a modem or an optical terminal. Essentially, it’s the gateway for bringing an external internet connection into the router and then to your network.
- LAN (Local Area Network): LAN ports on a router are designated for creating a network within a confined area, like a home, office, or school. They allow you to connect local devices directly to the router, enabling network access for computers, printers, televisions, and other smart devices.
- 10GE (10 Gigabit Ethernet): This high-speed Ethernet standard supports data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps. 10GE ports on routers facilitate faster data transmission, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks and connecting devices requiring high-speed internet connections.
10GE port on router: use, purpose
The 10GE (10 Gigabit Ethernet) port on a router is an advanced feature designed to cater to high-speed network requirements. Its functionalities can be expanded and diversified in several ways:
- Dual 10GE Ports: The presence of two 10GE ports on a Network Interface Card (NIC) allows for multiple connections. This setup enhances the network’s capacity by enabling simultaneous high-speed connections, ideal for setups requiring redundancy or increased bandwidth.
- 10 Gigabit WAN/LAN Port: These versatile ports can be configured as WAN inputs for connecting to an external internet source or as LAN outputs for distributing high-speed internet within the network. This flexibility is particularly useful in complex network environments with crucial high-speed internet input and distribution.
- 10 GE (10Gbps) SFP+ Port: SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable) ports are designed to install special modules that facilitate transport network connectivity. These ports are essential for connecting fiber optics and are typically used in enterprise-level networks where long-distance, high-speed connections are necessary.
- 10 GE RJ45/SFP+ Combo Port: This hybrid port supports two different connection standards – RJ45 and SFP+. While the technical input remains the same, the combo port offers the versatility of connecting either standard copper Ethernet cables (RJ45) or fiber optic cables (SFP+) based on the network requirements.
Incorporating these features into a router significantly enhances its functionality, making it adaptable for a wide range of high-performance network applications. Whether handling increased traffic, connecting to long-distance networks, or ensuring a fast and reliable internet connection, a router with these 10GE capabilities is well-equipped to meet the demands of advanced networking.
What is 10 GB Ethernet usually used for?
Once exclusive to professional-grade equipment, the 10GE (10 Gigabit Ethernet) ports have become increasingly relevant in the broader array of devices, including routers, servers, and data storage systems. This high-speed port is essential for transferring large volumes of information, a necessity in today’s data-driven world.
With the advent of high-speed WiFi standards like WiFi 6, integrating 10GE ports into routers has become more prominent. These ports are particularly crucial in industrial WiFi routers, which must support numerous simultaneous connections while maintaining high bandwidth for efficient operation.
In gaming and home routers, including 10GE ports seems excessive. However, given the relentless growth in internet traffic, the consumption of streaming video and audio services, and the increasing reliance on video surveillance, the relevance and demand for such high-speed ports are poised to rise.
The trend towards more data-intensive applications and the continuous increase in connected devices per household are pushing the limits of current network infrastructures. As a result, the presence of 10GE ports in home and gaming routers is becoming less of a luxury and a future-proofing necessity, ensuring that these devices can handle upcoming technological advancements and the escalating demands for faster, more reliable internet connectivity.
What is the throughput of 10GE?
Typically, 10GE (10 Gigabit Ethernet) ports offer a theoretical maximum data transfer rate of 10 gigabits per second, but actual speeds are usually slightly lower than this value. This is due to several factors:
Service Information Bits: During data transmission, a portion of the bandwidth is used for service purposes such as packet checksums, synchronizing pulses, and other protocol mechanisms. These elements are necessary to ensure proper and reliable data transmission, but they reduce user data’s available bandwidth.
Cable Quality and Length: The actual speed can also depend on the cables’ quality and the distance between connected devices. The higher the quality of the cable and the shorter the distance, the closer the speed will be to the maximum possible speed.
As a result, if there are no significant cable losses and quality equipment is used, the data transfer speeds on 10GE networks can approach 9 gigabits per second. This is true for most network ports, where the maximum speed declared by manufacturers usually does not include losses for service needs. This is important to consider when planning and configuring network infrastructure, especially in environments where high bandwidth is required for mission-critical applications.
Do I need 10gb Ethernet at home?
The decision to implement 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GE) in your home should be based on your unique requirements and usage patterns:
- 10GE Internet: While 10 Gigabit Ethernet may seem excessive for basic needs like streaming on a single TV, it becomes more relevant if you have multiple devices simultaneously downloading or streaming video. However, high-speed internet plans, such as 5 or 8 Gbit/s, are becoming more affordable. For instance, services like Google Fiber offer speeds up to 8 Gbps at around $150, making such speeds more accessible.
- Gaming and Streaming: For regular gaming or streaming high-definition video, 10 Gigabit Ethernet might be overkill. The current internet speeds of 1 Gbit/s are generally sufficient for these activities.
- Home Network Requirements: For a home network, even when setting up a home server for video streaming or recording from surveillance cameras, 10Gbit may be more than necessary. But since 1 Gbit/s might fall short for these tasks, opting for a 10GE network could be a consideration.
- Cost Considerations: It’s essential to weigh the costs of equipment and power usage when setting up a 10GE network to ensure you’re paying attention to your actual needs.
In summary, while a 10 Gigabit Ethernet network offers high speeds and future-proofing, it’s essential to balance these benefits against the practical requirements of your home setup and the associated costs. For most typical home uses, 10GE might be more than what’s needed, but it could be a justified investment for scenarios with multiple high-bandwidth devices or specialized home server setups.