What is USB?
With the development of computer technology was a question about the transfer of information between devices, the goal was to make them as universal. A primary goal was the question how to connect various devices to your computer as an example keyboard, mouse, and of course mobile phones. Initially, there were special connectors for each device but experience has shown that it does not quite convenient. To solve this problem was developed a universal serial bus (USB). Which has several versions (the natural development). The principle of operation is quite simple USB device is installed in a standardized chip producing the transformation of information obtained from the devices in a communication protocol that is passed in the form of digital information between two devices on the cable.
USB 2.0 vs 3.0 vs 3.1
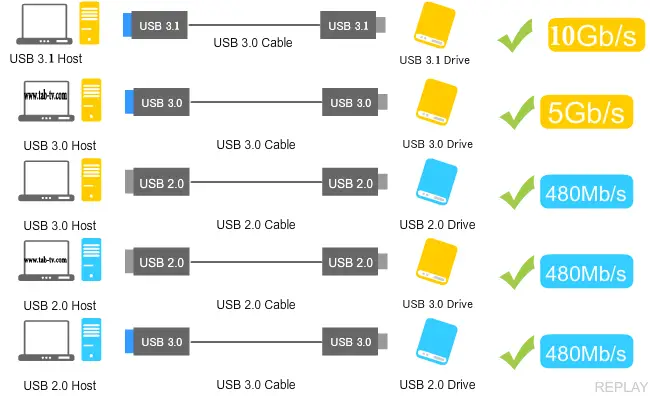
The main difference between the most common standards is the speed of information transfer between devices.USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports are compatible, but the transfer speed of the slowest port will be supported.
- USB 2.0 – 480Mbit/s
- USB 3.0 – 5Gb/s
- USB 3.1 – 10Gb/s
USB port versions
USB 1.0
USB 1.0 The first version of USB is the commercial name USB 1.0 and had a very low data transfer rate of only 1.5 Mbps, for example, the download speed was only 180 KB / s. But the developers of the standard used only 1 pair of wires, the second pair is used to transfer power, for example, to a device such as a keyboard up to 500 mA. The fifth served as a screen conductor. But the transmission speed was low and such ports were not widely used; later, an improved version was developed, which received the designation USB 2.0
Port USB 2.0
USB 2.0 retaining the same connectors, there are 6 types of USB connectors. USB 2.0 provided information transfer but already with a maximum speed of up to 480 m Bit / s, theoretically it is possible to transfer information at a speed of 60 m Bytes / s. Initially, power was also provided for 0.5A plug-in devices, but later they began to install current amplifiers to power power-hungry devices, and USB ones supporting 1A appeared, sometimes more often there were connectors with a maximum power output of 5A (USB 2.0 5A). Additional possibilities were invented, for example, direct connection of devices without a computer, for example, a telephone, camera or printer for printing photographs. Such a USB is not widely used, although it is used. But the developers did not stop there and life itself forced to think of how to increase the transmission speed. The introduction of ultra-high definition television played a role in this, and the existing USB 2.0 standard 4K could not provide the necessary information transfer speed. A new era has come, developed by USB 3.0
Port USB 3.0
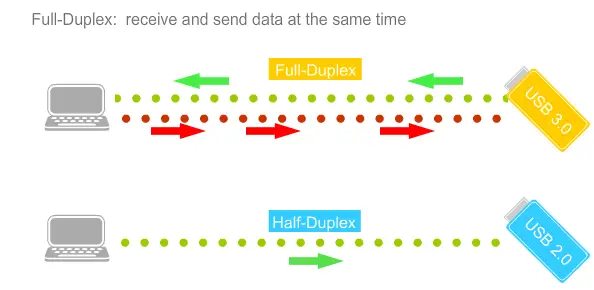
USB 3.0 in this connector, it was no longer possible to provide high speed with the same number of wires and the developers added additional wires for transmitting information, there were 9 wires plus a screen as a 10 wire, there were exactly 2 times more wires than in USB 2.0. Also, due to the increase in the number of pairs of wires, it has become possible to transmit information in full duplex, that is, simultaneously on one pair in one direction on the other to the other, which also increases the speed of information exchange.
To ensure compatibility has been saved previous location of the wires so that the devices have USB 2.0 connector can be easily connected to a USB 3.0 port and vice versa. This means that having such a flash drive it freely can be connected to a USB 3.0 port but the transfer speed will be at the level of USB 2.0. On the contrary a little more complicated as there are modifications of other types of connectors. But the same cables and connectors are compatible.
In order that the user could visually identify the USB 3.0 connector it is blue inside.
Port USB 3.0
USB 3.0 provides data transfer rate up to 5Gbit / s and can support devices draw up to 1 A.
Example of current loads imposed below, but any manufacturer can make their own adjustments upwards.
USB port specification, power supply
| Specification | Current | Voltage | Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB 1.x and 2.0 | 500 mA | 5 V | 2.5 W |
| USB 3.0 | 900 mA | 5 V | 4.5 W |
| USB 3.1 | 2 A | 5 V | 10 W |
| 5 A | 12 V | 60 W | |
| 5 A | 20 V | 100 W | |
| USB Battery Charging | 0.5–1.5 A | 5 V | 2.5–7.5 W |
| USB Power Delivery | 2 A | 5 V | 10 W |
| 3 A | 12 V | 36 W | |
| 3 A | 20 V | 60 W | |
| 5 A | 20 V | 100 W |
Port USB 3.1
USB 3.1 -USB 3.0 modification through new communication protocols increased bandwidth up to 10Gb / s.
Port USB (UWB)
Wireless USB (UWB) wireless data transmission protocol like WI-FI data transmission rate depends on the distance and the range from 480 Mbit / second to 10 feet and 110 Mbit / s to 33 ft.
Optical USB (USB 3.0)
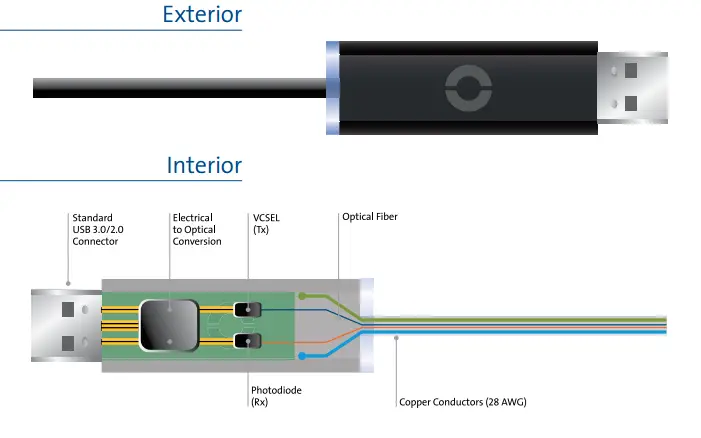
Optical USB (USB 3.0) some firms have realized that there are unoccupied niche as an optical signal transmission protocol USB. Invented transmit the USB cable and optical fiber. In this case, the converter is used with an electric signal into an optical and between terminals is transmitted optical signal, using the same protocol USB 3.0 but the signal is transmitted to the optical medium. One of the undeniable advantage of being able to create a very flexible cable and virtually unlimited length, cable length depends on the laser power built into the connector cables are now made up to 150 feet.