Selecting an appropriate television involves carefully considering various factors tailored to individual needs and usage patterns. The contemporary television market is diverse, featuring technologies such as Nano Cell, Neo QLED, and OLED, with price points ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. In some cases, high-end models can reach exorbitant prices.
For a pragmatic approach to television selection, it’s crucial to identify the primary purpose of the TV. Usage can vary significantly—ranging from casual viewing of television shows and engaging in gaming to streaming high-definition content from online services. This usage dictates the selection criteria.
An excessively high-end TV may not be necessary for casual viewing, as standard features might suffice. In contrast, gaming or streaming high-definition content often benefits from advanced features in higher-end models, like better refresh rates or enhanced color accuracy.
Thus, the guide to selecting a TV should focus on aligning the features of the TV with the intended use, ensuring a balance between cost and functionality. This approach ensures that the selected TV performs without unnecessary expenditure on extra features.
How to choose a TV with a good picture quality
When evaluating a television, picture quality is paramount, and the quality of the display is a critical determinant of this aspect. The hierarchy of display technologies in terms of picture quality is as follows:
- OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) Displays: At the pinnacle of image quality, OLED displays offer the highest standard, often called 100% quality. The hallmark of OLED technology is its ability to provide deep blacks and high contrast ratios, contributing to superior picture quality.
- QLED (Quantum Dot LED) Displays: These are advanced LED displays characterized by high-quality materials that enhance overall image quality, approximately 80% of what OLED offers. A critical factor in assessing QLED quality is color depth. Displays with 10-bit color depth are considered high quality, offering a more comprehensive color range and smoother gradients. Conversely, 8-bit + FRC (Frame Rate Control) displays are considered inferior. A refresh rate of 120Hz is a benchmark for quality in QLED displays, ensuring smoother motion and better performance in fast-paced scenes.
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode) Displays: Standard in terms of image quality, LED TVs vary in quality, typically ranging from 40-60% compared to OLED. Despite less impressive picture quality, LED TVs are more budget-friendly and can be a viable option for those looking for a cheaper TV.
In summary, the choice between OLED, QLED, and LED depends on the desired balance between picture quality and price. OLED offers the best quality but at a higher cost. QLED sits in the middle with good quality and reasonable pricing, and LED provides standard quality at more affordable prices.
Are OLED TVs worth it?
Whether OLED TVs are worth investing in depends on several factors, including your budget and whether you are willing to spend a few thousand dollars for a TV; if yes, then you can buy. Here are the pros and cons of OLED TVs.

- Advantages of OLED TVs: here are the main advantages of OLED TVs.
- Superior picture quality: OLED TVs are known for their exceptional picture quality, deep blacks, high contrast ratio, and vivid colors. This is due to the ability of each pixel to emit its light, allowing for precise control over brightness and color.
- Fast response times: OLED displays have speedy response times that reduce image blurring, making them ideal for viewing fast-moving content such as sports or video games.
- Disadvantages of OLED TVs: manufacturers don’t want to discuss the disadvantages, but they are there, and here’s a small list.
- Cost: OLED TVs typically cost more than LED or QLED TVs. This price difference can be a significant factor depending on your budget.
- Burn-in risk: Although modern OLED TVs are equipped with features that reduce this risk, there is still a risk of image burn-in when viewing static images for long periods. TVs have service programs to remove static images and correct brightness, but their possibilities are not endless.
- Brightness: While OLED TVs have excellent contrast, they may not be as bright as some LED/QLED models, which can be vital if you’re watching TV in a very bright room.
- Lifespan: OLED TVs have one naturally bad feature: over time, the organic diodes (pixels) degrade and lose their brightness, especially when overheated, so with heavy use, be prepared to replace your TV after 5-7 years.
In conclusion, OLED TVs offer some of the best picture quality. However, whether they are worth purchasing depends mainly on personal priorities and how much you value their benefits versus their higher cost.
Which brand of TV is best to buy?
Selecting the ideal TV brand is influenced by personal preferences, specific needs, and budget constraints. Various brands stand out for their distinct qualities, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Here’s an overview of some prominent brands, each with its unique strengths:
- Samsung: Notable for its QLED technology and, more recently, its venture into OLED since 2022, Samsung offers a diverse range of TVs across different price points. Its Tizen OS provides a wide array of applications. In 2022, Samsung divested its LED and QLED display factory to TCL, focusing more on OLED technology. While Samsung’s high-end models are reliable, their budget variants can be hit or miss, primarily due to variations in component quality.
- LG: A frontrunner in OLED technology since 2016, LG also offers QLED and LED TV options. Known for the popular WebOS platform, LG TVs boast a comprehensive selection of video streaming apps. LG, alongside Samsung, is often considered a top choice for quality and innovation in the TV market.
- Sony: Sony’s TVs are acclaimed for their exceptional color accuracy, motion processing, and overall picture quality, appealing especially to movie enthusiasts and sports viewers. Sony focuses heavily on building quality and software and outsourcing display manufacturing. Their TVs, powered by Google TV and Android, offer many applications, though they tend to be priced higher.
- Vizio: Vizio is a well-known brand offering budget-friendly TVs. While not groundbreaking in terms of innovation, Vizio TVs offer decent quality for their price. The brand primarily relies on large OEM manufacturers for production.
- TCL: Known for its budget-friendly offerings, TCL is a significant player in the TV manufacturing industry, including OEM production. TCL TVs are recognized for their balance of affordability and quality.
- Panasonic: Panasonic has seen a decline in its TV market presence, withdrawing from the US in 2014 and Canada in 2020. While some budget models are OEM-produced, their mid-range models are self-manufactured. Panasonic TVs are well-regarded but face stiff competition in pricing.
- Hisense: A major Chinese electronics firm, Hisense produces a substantial volume of TVs, including for other brands, as an OEM manufacturer. After acquiring Toshiba’s imaging division, Hisense has improved its TV quality. However, the brand offers various models with varying operating systems, necessitating careful consideration.
In summary, brands like LG and Samsung lead in high-end picture quality, Sony excels in performance and build quality, while TCL and Vizio are strong contenders in the budget segment. Panasonic and Hisense offer competitive options, though with specific considerations. The best brand for an individual depends on their viewing preferences, desired features, and budget.
How to choose the best screen resolution
Television image quality is fundamentally determined by the resolution, which refers to the total number of pixels that compose the image. Pixels, the tiny dots that form images, are crucial in defining the sharpness and clarity of what you see on the screen. The resolution is calculated by multiplying the number of horizontal pixels by the number of vertical pixels. Currently, there are three main resolutions for TVs:
- FULL HD (1920 x 1080): This resolution is now considered standard, providing precise and detailed images for everyday viewing.
- 4K UHD (3840 x 2160): Offering four times as many pixels as FULL HD, 4K UHD TVs deliver significantly sharper and more detailed images, especially noticeable on larger screens. This enhanced resolution allows for more precise viewing, even with close-up or zoomed-in content.
- 8K UHD (7680 x 4320): With sixteen times more pixels than FULL HD, 8K UHD TVs provide an incredibly high level of detail. However, this technology is still emerging and comes at a premium cost.
HD resolution, usually found only in inexpensive TVs, is an outdated format; such displays are made on old production lines at least ten years old. While FULL HD resolution suffices for most viewers, the increasing availability of 4K content from streaming services like Netflix and YouTube makes 4K UHD TVs a more future-proof choice. Considering the average TV replacement cycle of 7-10 years, investing in a 4K UHD TV ensures that your device remains relevant and can display the latest content for years. However, 8K content still needs to be improved in availability and commercial application, and the high cost of 8K TVs still needs to justify their purchase for most consumers. Therefore, a 4K UHD TV currently represents the best balance between cost, longevity, and picture quality.
Choosing a new TV with HDR
Understanding HDR (High Dynamic Range) is crucial when considering TV picture quality. HDR technology dramatically enhances the visual experience through a higher contrast ratio – the difference between an image’s darkest and brightest parts. A higher contrast ratio produces deeper blacks and brighter whites, resulting in an image that looks very similar to the real thing.
HDR is becoming an increasingly important factor in television technology. Whereas in the past, the focus was on display types and resolution, manufacturers now emphasize HDR capabilities. HDR exceeds the limitations of SDR (Standard Dynamic Range), which is commonly used in general broadcast and video, by providing finer and more detailed brightness levels.
However, it’s essential to know some of the nuances of HDR technology. As detailed in our article about Quantum HDR in Samsung TVs, many manufacturers use unique marketing names for HDR. Rather than paying attention to these names, it’s more important to ensure your TV can support HDR.
You should know that all manufacturers are cheating with HDR: the fact is that initially, according to the UHD Alliance’s UHD specification, it was supposed that true HDR could only be in TVs with UHD resolution and 10-bit color depth, and these are only premium TVs. But since most TVs produced do not meet this requirement, other alliances have emerged, such as Vesa DisplayHDR, which has come up with different parameters, and even a display with an 8-bit matrix that can not work with HDR at all can get the HDR400 logo.
TV manufacturers use different HDR formats such as HDR10, Dolby Vision, HLG, and HDR10+. While individual formats were more prevalent in the early days of HDR technology, modern TVs often support multiple HDR formats. So, the key is to check for HDR support, not a specific format.
Given the trend toward more HDR content, choosing an HDR-enabled TV is a forward-thinking choice. It ensures that your TV remains compatible with evolving content standards, extending its relevance and lifespan in the fast-paced world of digital entertainment.
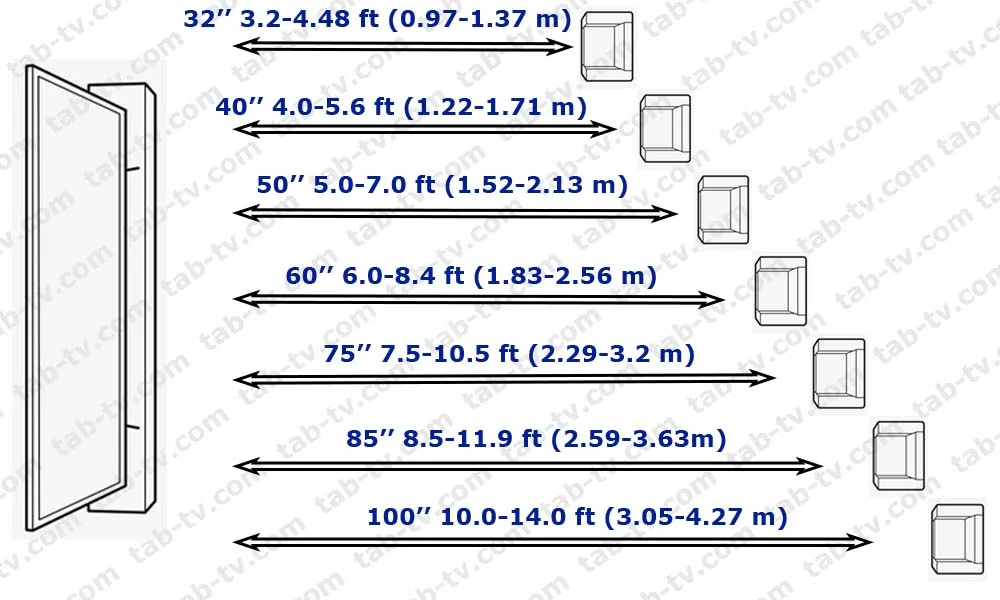
What TV size do you need?
The trend in home TVs is toward larger TVs, typically 32 to 85 inches diagonally. When choosing a TV, it is essential to consider the viewing distance in your room. To understand how your TV’s physical height and width relate to the diagonal screen size, check out resources such as “TV Size by Diagonal.”
The basic rule of thumb is to choose the largest TV that will fit comfortably in your room. According to current market trends, a 65-inch TV is a popular choice. This size balances the viewing experience and adapts to the size of most rooms. For more specific advice on choosing a TV based on the size of your room, you may find the article “TV viewing distance based on screen size” helpful. This resource can offer a clearer perspective on choosing a TV that fits your viewing environment.
What to avoid when buying a TV?
When shopping for a TV, there are a few pitfalls to avoid to make an informed decision that suits your needs and preferences:
- Ignoring screen technology: Choosing a TV with lower resolution or outdated screen technology may save you money initially but can lead to dissatisfaction, especially when higher resolution content becomes more prevalent. Here’s a little tip on how to test screen quality: go to a store with a showroom and a lot of TVs running. Stand in front of the television and then move to the side, simulate viewing from the side; you will notice that some televisions have an extreme decrease in brightness when viewed from the side. This indicates the screen quality; most likely, the screens in such televisions are made using old technology.
- Neglect of input delay and refresh rate (for gamers): If you plan to use your TV for gaming, low input lag and high refresh rate are crucial for a smooth gaming experience. These features are necessary to avoid noticeable lags and motion blur.
- Fall for marketing gimmicks: Beware of attractive marketing terms and buzzwords that offer no tangible benefits. Research and understand what features are essential to your browsing needs.
- Operating system neglect: The user interface and app ecosystem varies from TV operating system to TV operating system (e.g., Android TV, WebOS, Tizen). Choose one that is easy to use and supports your preferred streaming services.
Find out what generation of OS is in the TV; this is especially critical in cheap TVs. If Samsung, LG, and Sony update their OS every year, other manufacturers may offer TVs with outdated OS. For example, you might see a 2023 TV with Android TV OS version 9, but that version was released in 2018; in 2022, Android TV version 13 has already been released. Here are some resources to help you navigate OS versions.






